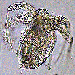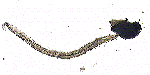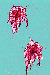Planktonic Animals
Be sure to write about what you are learning in the lab section of your notebook. You will be expected to answer questions about the lab activity during the lab self test and lab quiz. It helps to have your text and coloring books open beside you for support.
| Refer to the Assigned Readings Below: | |
| Marine Biology Textbook | Chapter 15, pages 328 to 336 |
| Marine Biology Coloring Book | Plates 24, 35, 78 to 81, 83 and 84 |
Holoplankton are species of invertebrates that spend their entire lives from hatching until death as plankton.
Some species of invertebrates have their embryonic development in the plankton and become planktonic adults. These species spend their entire lives in the plankton. They are the most abundant type of zooplankton.
|
Holoplanktonic Crustacea
|
|
|
Copepods are tiny holoplanktonic crustaceans. Copepods make up over 90% of the zooplankton by number and are the most abundant marine animals. |
Observe the photograph of a copepod. |
|
Observations:
|
|
|
Holoplanktonic Copepod Diversity
|
|||||||
|
Copepods are diverse as well as abundant. A typical zooplankton sample will contain several different species. |
|||||||
Experimental
Set Up:
|
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
Observations:
|
|||||||
|
Holoplanktonic Predator
|
|||||||
|
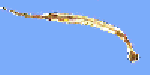
Arrow worms are holoplanktonic invertebrates which feed on copepods. They are fast swimmers and can easily capture their prey. |
|||||||
Experimental
Set Up:
|
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
Observations:
|
|||||||
|
Gelatinous Holoplankton
|
|||||||||||||
|
There are several types of holoplanktonic species whose bodies are jelly-like. They are called gelatinous zooplankton. These forms include medusae, siphonophores, salps and larvaceans. |
|||||||||||||
Experimental
Set Up:
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
Observations:
|
|||||||||||||
|
Additional Gelatinous Plankton
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Gelatinous zooplankton include medusae, ctenophores and siphonophores. |
||||||||||||||||
Experimental
Set Up:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Observations:
|
||||||||||||||||
Meroplankton are the planktonic larvae of nektonic or benthic species.
Some species of invertebrates spend their adult lives on or in the benthos but their embryos develop in the plankton. Some species of fishes spend their adult lives as nekton but their eggs and embryos develop in the plankton. These planktonic larvae act as a dispersal stage being distributed by currents to new sites where they settle to the bottom and grow into adults.
|
Meroplanktonic Crustacean Nauplii
|
||||
|
Barnacles live cemented to hard substrates as adults but their larval stages are meroplanktonic. |
||||
Experimental
Set Up:
|
||||
|
||||
|
Observations:
|
||||
|
Meroplanktonic Echinoderm Larvae
|
|||||
|
Starfish live on the benthos as adults but their embryos develop in the plankton. The embryo passes through two distinct stages before its final metamorphosis. The bipinnaria larva grows into a brachiolaria larva which is ideally suited to life in the plankton. These meroplanktonic larvae undergo dramatic changes as they metamorphose. |
|||||
Experimental
Set Up:
|
|||||
|
|||||
|
Observations:
|
|||||
|
Meroplanktonic Larvae
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Many meroplanktonic larvae look very different from the adult forms they develop into. Many were misidentified by marine biologists who described them as different species. These mistakes were corrected once developmental sequences were clarified. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental
Set Up:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Observations:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demersal plankton are species that live in the sea bottom during the day but rise up into the plankton at night.
Demersal species are temporary members of the plankton and are taken by plankton nets in shallow waters throughout the night.
|
Demersal Crustacea
|
|
| Amphipods are crustaceans which may be planktonic or benthic. Some species are demersal plankton. |
Observe the photograph of an amphipod. |
|
Observations:
|
|
Lab Activity 11.4 Zooplankton Identification