- phoenix college
> departments > Liberal
Arts
> economics
> ECN112>
Ch. 6 Questions
- Dr. Bromley
ECN112
(Microeconomics):
Additional
Multiple Choice
Questions
Chapter 6
Correct answers are indicated by
underlined letter.
All contents are ©2000 by Ray Bromley
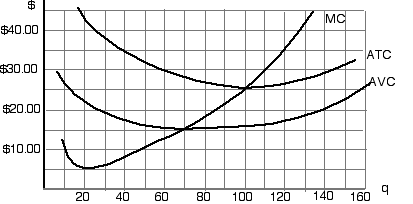
Above are cost curves of Wilbur Write's Paper Co., one of many
companies that make plain white copier/printer paper. Suppose
Wilbur Write's Paper Co. acts as a price taker. The quantities
shown represent reams of paper sold each day (each package containing
100 sheets), and the dollar amounts represent the costs of each
package, in the short run. Answer questions 1-15 using the above
diagram.
6-1 If the company acts as a price taker, what price will it charge
in the short run?
A. $5.00
B. $15.00
C. $25.00
D. $30.00
E. Can't tell
6-2 What is the lowest market price that will make it worthwhile
for Wilbur Write's Paper Co. to produce output in the short run?
A. $5.00
B. $15.00
C. $25.00
D. $30.00
E. Can't tell
6-3 What is the lowest market price that will enable the company.
to make a profit in the short run?
A. $5.00
B. $15.00
C. $25.00
D. $30.00
E. Can't tell
6-4 We know that if Wilbur Write's Paper Co. produces any paper
at all, it will produce at least (approximately)
A. 20
B. 70
C. 80
D. 100
E. 120
6-5 If the market price of paper is $40.00 per ream, what can
you say about Wilbur Write's Paper Co.'s profit?
A. The company makes a loss.
B. There is neither profit or loss.
C. Profit is positive, but less than $550.
D. Profit is more than $550, but less than $1200.
E. Profit is more than $1200.
6-6 If the market price of paper is $35.00 per ream, what can
you say about Wilbur Write's Paper Co.'s profit?
A. The company makes a loss.
B. There is neither profit or loss.
C. Profit is positive, but less than $550.
D. Profit is more than $550, but less than $1200.
E. Profit is more than $1200.
6-7 If the market price of paper is $30.00
per ream, what can you say about Wilbur Write's Paper Co.'s profit?
A. The company makes a loss.
B. There is neither profit or loss.
C. Profit is positive, but less than $550.
D. Profit is more than $550, but less than $1200.
E. Profit is more than $1200.
6-8 If the market price of paper is $25.00 per ream, what can
you say about Wilbur Write's Paper Co.'s profit?
A. The company makes a loss.
B. There is neither profit or loss.
C. Profit is positive, but less than $550.
D. Profit is more than $550, but less than $1200.
E. Profit is more than $1200.
6-9 If the market price of paper is $20.00 per ream, what can
you say about Wilbur Write's Paper Co.'s profit?
A. The company makes a loss.
B. There is neither profit or loss.
C. Profit is positive, but less than $550.
D. Profit is more than $550, but less than $1200.
E. Profit is more than $1200.
6-10 If the market price is $35.00, what will be Wilbur Write's
Paper Co.'s output (approximately)?
A. 0
B. 40
C. 120
D. over 160
E. Can't tell
6-11 If the market price is $30.00, what will be Wilbur Write's
Paper Co.'s output (approximately)?
A. 0
B. 60
C. 110
D. 145
E. Can't tell
6-12 If the market price is $25.00, what will be Wilbur Write's
Paper Co.'s output (approximately)?
A. 0
B. 15
C. 100
D. 155
E. Can't tell
6-13 If the market price is $20.00, what will be Wilbur Write's
Paper Co.'s output (approximately)?
A. 0
B. 25
C. 85
D. 140
E. Can't tell
6-14 If the market price is $15.00, what will be Wilbur Write's
Paper Co.'s output (approximately)?
A. 0
B. 25
C. 70
D. 140
E. Can't tell
6-15 If the market price is $10.00, what will be Wilbur Write's
Paper Co.'s output (approximately)?
A. 0
B. 25
C. 55
D. 140
E. Can't tell
6-16 Which of the following best describes a long run equilibrium
in a competitive industry?
A. MC = MR < P = ATC
B. MC = MR = P = ATC
C. MC = P > MR = ATC
D. P = MC > MR < ATC < P
E. P = MC = ATC > MR
Tommy's Tomatoes is one of many roadside stands that sell tomatoes
along a two-mile stretch of California highway in the tomato-growing
region. All of the stands post large signs which say "tomatoes
25 cents per pound." The tomatoes sold by Tommy's are no
different from those sold at the other stands. Questions 17-18
pertain to Tommy's stand.
6-17 Based on the information above, you know the stand is
A. a price taker.
B. a natural monopolist.
C. a cartel.
D. a price searcher.
E. able to charge whatever price it wishes.
6-18 Suppose you know that the costs of having someone watch the
stand and keeping it stocked with fresh picked tomatoes average
out to about 23 cents per pound sold. What can you say?
A. The stand should lower price to increase sales.
B. The stand should shut down, since obviously it is not making
a profit.
C. The stand should be open for business.
D. The stand should raise price.
E. The stand should reduce output.
6-19. Suppose that the stand is currently operated for as long
as it takes to sell all of the tomatoes picked each day. More
tomatoes could be picked than are being picked daily now. Also,
the people operating the stand could be asked to stay later, at
the same rate of pay, than they do on a typical day now. What
other information would enable you to determine if picking and
selling more tomatoes would be sensible?
A. the average fixed cost
B. the average total cost
C. the wage of the people working at the stand
D. the marginal cost of picking and selling the tomatoes
E. the average variable cost
6-20 Which kind of firm has a horizontal demand curve?
A. A price taker in a competitive industry.
B. Only those price takers that have low average total costs.
C. A price taker, but only if the industry demand curve is horizontal.
D. Any seller.
E. A seller which is a big part of the market and which produces
a unique good.
6-21 In the long run...
A. perfectly competitive firms, in theory, make no economic profit.
B. firms are free to alter capital, and therefore their firms'
size.
C. price will be equal to minimum long run ATC in a perfectly
competitive industry.
D. entry and exit can occur in a perfectly competitive industry.
E. all of the above.
6-22 In the short run, the relationship between the individual
firm's supply curve and the competitive market supply curve is
A. the market supply curve is the summation of all of the
individual firms' supply curves.
B. the market supply curve is equal to the average of the individual
firms' supply curves.
C. the individual firms have horizontal supply curves, but the
market curve is upward-sloping.
D.the individual firms have vertical supply curves, but the market
curve is upward-sloping.
E.the individual firms have upward-sloping supply curves, but
the market curve is horizontal.
6-23 If the firms in a perfectly competitive
price taker industry were facing costs that were less than the
prices they were charging, the firms
A. would receive short run economic profits that would be offset
by long run economic losses.
B. would face new competition in the long run, which would
force price down to the level of costs.
C. would receive short-run economic profit and long-run economic
profit.
D. must be colluding or rigging the market in some way.
E. would receive small economic profits in the short run, and
even larger economic profits in the long run.
6-24 If romaine lettuce is produced by price takers, a decrease
in demand for lettuce will
A. induce new, more efficient producers of lettuce to enter the
market in the long run, if it is perfectly competitive.
B. cause the existing firms in the industry to expand i the long
run.
C. induce both new and existing producers to bid resources away
from other uses.
D. encourage owners of resources now used to produce lettuce
to move their resources into other uses in the long run.
E. cause producers of lettuce to make losses in the long run.
6-25 The actions of a firm in perfect competition have no effect
on product price. Thus, the demand curve faced by a singe firm
is
A. a horizontal line at the level of market price.
B. a downward-sloping line.
C. the firm's marginal cost curve.
D. the firm's total revenue curve.
E. impossible to determine.
6-26 Assume that corn is produced by price takers in a competitive
industry. The government tries to boost farmers' profit by fixing
the price of corn above the equilibrium level and buying any surpluses
thus produced. In the long run, corn farmers will
A. expand production of corn, raising the prices of resources
used in growing corn.
B. expand production of corn and make long-term profits.
C. sell more corn to non-governmental buyers because of the higher
price.
D. produce less corn because of the higher price and lower quantity
demanded.
E. produce less corn because the prices of resources used to produce
wheat will rise.
6-27 If a producer is only covering variable costs plus a third
of fixed costs, what should she do in the short run?
A. Shut down immediately and liquidate her assets in the long
run.
B. Shut down and liquidate her assets immediately, since she is
making losses.
C. Continue to produce as long as variable costs are covered.
D. Continue to produce as long as marginal costs are covered.
E. Continue to produce, recognizing that economic profits do not
include fixed costs.
6-28 A firm should shut down (produce no output) if
A. price is below marginal cost.
B. price is below average fixed cost.
C. price is below average variable cost.
D. price is below average total cost.
E. price is below minimum marginal cost.

6-29 Based on the diagram above and assuming the firm is a price
taker, the firm will choose to operate in the short run if price
is just above
A. 3
B. 8
C. 14
D. 15
E. can't tell
6-30 Based on the diagram above and assuming the firm is a price
taker, the firm will make a profit in the short run if price is
just above
A. 3
B. 8
C. 14
D.15
E. can't tell
6-31 Based on the diagram above, a price-taker firm will (in the
short run) produce an output level of
A. 15
B. 40
C. 50
D. 10
E. can't tell
6-32 Based on the diagram above, if price is $15, a price-taker
firm will produce an output level of
A. 15
B. 40
C. 50
D. 10
E. more than 50
6-33 Based on the diagram above, the perfectly competitive firm
is both productively and allocatively efficient if price is
A. 3
B. 8
C. 14
D.15
E. can't tell
6-34 Based on the (short run) diagram above, if price is $15,
the perfectly competitive firm will be in long run equilibrium
only if
A. other firms leave the industry
B. demand for the industry's good increases.
C. the firm invests in cost-cutting equipment.
D. market supply increases.
E. the firm reduces it's size.
6-35 The manager of a store selling purified water to people who
bring and fill their own bottles realizes that her marginal costs
exceed her marginal revenues. This means that
A. the firm must not be a price taker.
B. producing more output would reduce the profit or enlarge
the loss of the firm.
C. the manager must be maximizing profit right now.
D. the firm should shut down and cease production in the short
run.
E. the firm is not covering its variable costs.
6-36 Suppose that the demand curve for playing
cards is downward-sloping and that the cards are produced in a
constant-cost industry (which is perfectly competitive). If a
50-cent per deck tax is imposed on each pack of cards, by how
much will the (buyer's) price of a deck of cards change in the
long run and in the short-run?
short run long run
A. 50 cents more than 50 cents
B. less than 50 cents more than 50 cents
C. less than 50 cents 50 cents
D. less than 50 cents less than 50 cents
E. 50 cents less than 50 cents
6-37 Daffy D.'s Wiener Company sells Daffy Dogs (with mustard,
onions, and chili) for $1.75 a piece. Daffy D. can sell as much
as he wants to at this price, but his output does not really affect
the price, since Daffy faces stiff competition from Bugs' Bun
Eat, and other hot dog stands located nearby. Daffy's marginal
cost is $1.75 per Daffy Dog, and minimum average variable cost
is estimated to be about $1.80 per Daffy Dog. What advice can
you give Daffy?
A. "Increase your output, Daffy!"
B. "Continue to operate as you now do!"
C. "Shut down, Daffy!"
D. "Cut back your output, Daffy!"
E. "I can't tell you anything without more information!"
3-38 Bart's Have a Cow Company sells Bart Burgers (with choice
of catsup or ketchup) for $1.50 a piece. Bart can sell as much
as he wants to at this price, but his output does not really affect
the price, since Bart faces stiff competition from "60 Minute
Burger," and other burger restaurants in the area. Bart's
marginal cost is $1.50 per Bart Burger, and average variable cost
is estimated to be about $1.45 per Bart Burger. What advice can
you give Bart?
A. "Aye carramba! Shut down, Bart!"
B. "Doh! Cut back your output, Bart!"
C. "Don't have a cow, man! Increase your output, Bart!"
D. "Excellent. Continue to operate as you now do!"
E. "Eat my shorts! I can't tell you anything without more
information!"
6-39 In perfect competition (which is a price-taker market),
A. the supply curve for the industry is always upward sloping
in the long run.
B. the supply curve for the firm is its entire average variable
cost curve, in the short run.
C. the long-run supply curve for the firm is the upward-sloping
part of marginal cost.
D. short run supply curve for the industry is horizontal.
E. short run supply curve for the industry is the horizontal
sum of the firms' MC curves (above AVC).
6-40 Which of the following would you expect to be horizontal?
A. Market (industry) demand for price takers in the short run.
B. Market (industry) demand for price takers in the long run.
C. Short run market (industry) supply for price takers in a constant
cost industry.
D. Short run market (industry) supply for price takers in a constant
cost industry.
E. Long run market (industry) supply for price takers in
a constant cost industry.
back to top
- phoenix college
> departments > Liberal
Arts
> eonomics
> ECN112>
Ch.6 Questions
All content on this page is ©2000 by Ray Bromley
- updated 4/16/00 by Ray
Bromley
- disclaimer
Chapter 5 Questions

